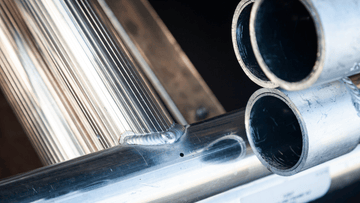
Ever found yourself battling against porosity and cracking while welding cast aluminum? You're not alone in the struggle. These common issues can test the patience of even the most skilled welders and jeopardize the quality of your projects. Yet, what if these obstacles could be the keys to fine-tuning your welding process?
Our guide offers practical solutions to common problems when working with cast aluminum. We'll cover essential preparation, precise welding techniques, and post-weld processes to help you achieve clean, strong welds that stand the test of time.
Keep reading to discover how to deliver professional-grade results on your next welding project.
Welding Cast Aluminum: The Basics
When it comes to welding cast aluminum, there are a few basics that you need to keep in mind to ensure a successful weld. Here are some key points to remember:
Material Preparation
Before you start welding, it's important to properly prepare the material. This includes cleaning the area to be welded, removing any surface contaminants, and preheating the material if necessary. Preheating can help prevent cracking and improve weld penetration.
Filler Material
Choosing the right filler material is crucial for a strong, durable weld. For cast aluminum, it's recommended to use a filler material with a lower melting point than the base material. This helps prevent the base material from melting and weakening the weld.
Welding Technique
When welding cast aluminum, it's important to use a technique that minimizes the heat input and prevents warping. TIG welding is often the preferred method, as it allows for precise control of the heat input. It's also important to maintain a consistent travel speed and avoid overheating the material.
Post-Weld Treatment
After welding, it's important to properly treat the material to ensure a strong, durable weld. This includes stress relieving, which involves heating the material to a specific temperature and allowing it to cool slowly. This helps reduce internal stresses and prevent cracking.
Preparation for Welding
Cleaning and Degreasing
Before welding cast aluminum, make sure the surface is clean and free of any contaminants such as dirt, oil, or grease. Failure to do so can result in poor-quality welds that may fail under stress.
To clean the surface, use a wire brush or sandpaper to remove any loose debris or oxidation. Afterward, use a degreaser to remove any oil or grease. Be sure to rinse the surface thoroughly with clean water and allow it to dry completely before proceeding with welding.
Preheating Procedures
Preheating is a critical step in welding cast aluminum. It helps to reduce the risk of cracking and ensures that the weld is strong and durable.
To preheat the metal, use a propane torch or an oven to heat the surface to a temperature of between 300 and 400 degrees Fahrenheit. Be sure to heat the entire area that will be welded evenly. After preheating, allow the surface to cool to room temperature before beginning the welding process.
Welding Techniques
When welding cast aluminum, two popular methods are TIG welding and MIG welding. Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the application and the skill level of the welder.
TIG Welding Method
TIG welding is a popular method for welding cast aluminum due to its precision and ability to produce high-quality welds. TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode to create an arc that melts the aluminum, while a filler rod is added to the weld pool to create a strong joint.
To achieve a successful TIG weld on cast aluminum, you need to follow a few key steps:
- Clean the surface of the aluminum thoroughly to remove any dirt, oil, or other contaminants that may affect the weld quality.
- Preheat the aluminum to reduce the risk of cracking and improve weld penetration.
- Use a filler rod that matches the composition of the aluminum to ensure a strong joint.
- Maintain a consistent arc length and travel speed to produce a uniform weld bead.
MIG Welding Approach
MIG welding is another popular method for welding cast aluminum. It is faster and more efficient than TIG welding, making it a good choice for large projects or production work. MIG welding uses a wire electrode that is fed through a spool gun, which melts the aluminum and creates a strong joint.
To achieve a successful MIG weld on cast aluminum, you need to follow a few key steps:
- Clean the surface of the aluminum thoroughly to remove any dirt, oil, or other contaminants that may affect the weld quality.
- Adjust the MIG welder settings to match the thickness of the aluminum and the wire diameter.
- Use a filler wire that matches the composition of the aluminum to ensure a strong joint.
- Maintain a consistent wire feed speed and travel speed to produce a uniform weld bead.
Welding Challenges and Solutions
Porosity Issues
Welding cast aluminum can be challenging due to the porosity issues that often arise. Porosity is caused by the presence of gas bubbles in the weld, which can weaken the joint and cause it to fail. To prevent porosity, you need to ensure that the aluminum is clean and free of any contaminants.
This can be achieved by using a wire brush or grinder to remove any dirt or oxidation from the surface of the aluminum. You can also use a shielding gas, such as argon, to prevent the formation of gas bubbles by displacing the air around the weld.
Cracking Prevention
Another challenge when welding cast aluminum is the potential for cracking. This is often caused by the high heat input required for welding, which can cause the aluminum to warp and distort. To prevent cracking, you need to use a low heat input and to preheat the aluminum before welding.
You can also use a filler material that is compatible with the aluminum being welded to reduce the stress on the joint and prevent cracking. Additionally, using a post-weld heat treatment can also help to reduce the likelihood of cracking.
Post-Welding Processes
Cooling and Solidification
After welding cast aluminum, it is crucial to allow the material to cool and solidify properly. This process is important because it ensures that the welds are strong and durable. The cooling process should be done gradually to prevent any thermal shock that may cause cracking or distortion.
One way to ensure a proper cooling process is by using a post-weld heat treatment. This process involves heating the welded area to a specific temperature and holding it there for a set amount of time. The heat treatment can help to relieve any residual stress and improve the overall strength of the weld.
Finishing and Machining
Once the cast aluminum has cooled and solidified, it is time to finish and machine the welded area. This process involves removing any excess material and smoothing out the surface of the weld.
It is important to note that welding cast aluminum can be challenging due to its low melting point and high thermal conductivity. Therefore, it is recommended to use specialized equipment and techniques to achieve a high-quality weld. Additionally, it is crucial to follow proper safety procedures when welding, as aluminum can produce harmful fumes and dust.
Conclusion
Conquering the art of welding cast aluminum is an achievable feat, and with the guidance shared here, you're now better equipped to tackle the hurdles it presents. Remember, the key lies in patience, precision, and practice. By methodically applying the techniques we've covered—from meticulous preparation to the careful selection of filler materials—you can rise above the challenges and secure welds that not only hold firm but also display your commitment to quality craftsmanship.
As you apply these newfound strategies to your workbench, embrace each task as an opportunity to refine your skills. Cast aluminum welding may test your patience, but it's a test that brings great rewards in skill advancement and professional growth. So go forth with confidence, and let your welds be a testament to the expertise you've honed through diligence and dedication.
While you’re here, make sure not to miss our best welding machines collection. ArcCaptain offers a wide array of welders and other equipment to meet every professional welder’s needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can cast aluminum be welded?
Yes, cast aluminum can be welded. However, it requires special techniques and equipment to achieve a successful weld.
Why is cast aluminum hard to weld?
Cast aluminum is hard to weld because it has a high thermal conductivity, which means it dissipates heat quickly. It also has a tendency to crack or warp during the welding process due to its high porosity and low ductility.
Can you weld cast aluminum with a stick welder?
Welding cast aluminum with a stick welder is not recommended. Stick welding produces a lot of heat, which can cause the aluminum to warp or crack. It is also difficult to control the heat input, which can result in a poor-quality weld.
How can you tell the difference between cast aluminum and aluminum?
Cast aluminum has a rougher surface texture than regular aluminum. It also has a more porous appearance due to the casting process. Additionally, cast aluminum is typically heavier than regular aluminum.
Do you pre-heat cast aluminum before welding?
Pre-heating cast aluminum before welding is recommended. This helps to reduce the risk of cracking and warping during the welding process. The pre-heat temperature will depend on the thickness of the material and the welding method being used.
Can you MIG weld cast aluminum?
Yes, you can MIG weld cast aluminum. However, you'll need a specialized aluminum MIG welder and a shielding gas like argon or helium. It's also important to use the correct wire and settings for the material being welded.
