What is oxy-acetylene welding? This method uses a high-temperature flame to melt and join metals. It combines oxygen and acetylene gas in a specialized torch, producing a flame that reaches up to 3,500 degrees Celsius.
This intense heat melts metal edges, and a filler rod is added to bond the pieces. Oxy-acetylene welding is versatile, suitable for both welding and brazing. It's particularly effective for thin metals and can be used on various materials including steel, cast iron, and copper.
While it requires practice to master, it's a valuable skill for metalworking. The technique offers precise control and is useful for repairs and artistic projects. Continue reading to explore the intricacies of oxy-acetylene welding.
What Is Oxy-Acetylene Welding?
Oxy-acetylene welding, also known as gas welding, is a process that involves the use of a flame produced by the combustion of oxygen and acetylene gases. The process is commonly used for welding and cutting metals, and it is known for its versatility and portability. The flame produced by the combustion of the gases can be easily adjusted to suit the requirements of the welding job.
Understanding the Oxy-Acetylene Process
The process involves the use of an oxy-acetylene torch, which is a hand-held tool that combines oxygen and acetylene gases to produce a flame. The torch is used to heat the metal to be welded, and a filler rod is used to add material to the joint.
The flame produced by the torch melts the metal, and the filler rod is used to fill the gap between the two pieces of metal.
Oxy-acetylene welding is known for its ability to weld a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper. The process is also used for brazing, which involves joining two pieces of metal using a filler material that melts at a lower temperature than the metal being joined.
Historical Background and Development of the Oxy-acetylene Welding Process
The oxy-acetylene welding process was first developed in 1903 by French engineers Edmond Fouche and Charles Picard. The process involved the use of pure oxygen instead of air to increase the temperature of the flame, which made it possible to weld metals more effectively.
Over the years, the oxy-acetylene welding process has undergone several improvements, including the development of new torch designs and the use of different gases, such as propane and natural gas. Today, the process is widely used in the metalworking industry and is considered one of the most versatile and effective welding processes available.
The 5 Components of the Oxy-Acetylene Welding Setup
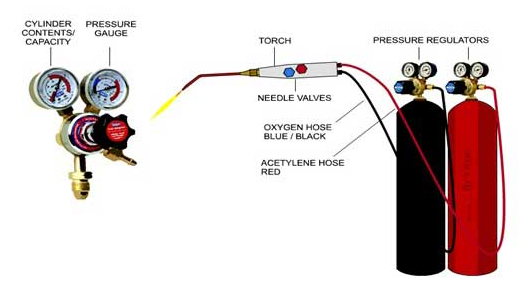
To perform oxy-acetylene welding, you need specific equipment. Here's an overview of the equipment used in oxy-acetylene welding:
1. Oxygen and Acetylene Gas Cylinders
Oxygen and acetylene gas cylinders are the most critical components of the oxy-acetylene welding setup. The oxygen cylinder is colored green and the acetylene cylinder is colored maroon. These cylinders are filled with compressed gases that are used to generate the flame required for welding.
2. Regulators
The regulators are used to control the pressure of the gases that are flowing from the cylinders. The oxygen and acetylene regulators are separate and are attached to their respective cylinders. The regulators ensure that the gases are delivered at a constant and safe pressure.
3. Hoses
The hoses are used to connect the regulators to the torch. The hoses used in oxy-acetylene welding are made of durable materials that can withstand the high pressure of the gases. They are color-coded to avoid confusion, with the oxygen hose being green and the acetylene hose being red.
4. Torch
The torch is the device that generates the flame required for welding. The torch consists of a handle, mixer, and tip. The mixer is where the oxygen and acetylene gases are mixed in the correct proportion to create the flame. The tip is where the flame is emitted.
5. Safety Gear
Safety gear is an essential component of the oxy-acetylene welding setup. It includes protective clothing, gloves, goggles, and a welding helmet. The protective clothing is designed to protect your skin and clothing from the heat and sparks generated during welding. The gloves protect your hands, while the goggles and welding helmet protect your eyes and face from the intense light and heat of the welding flame.
Applications of Oxy-Acetylene Welding
Oxy-acetylene welding is a versatile welding process that finds its application in various industries such as automotive repair, metal fabrication, and art. Here are some of the applications of oxy-acetylene welding:
1. Automotive Repair
Oxy-acetylene welding is commonly used in automotive repair shops for repairing and fabricating exhaust systems, repairing fenders and body panels, and fixing frames. The high temperature produced by the oxy-acetylene flame allows for precise and controlled welding of thin metal sections.
2. Metal Fabrication
Oxy-acetylene welding is widely used in the metal fabrication industry for welding and cutting metal. It is used for welding pipes, tubes, and other metal components. The welding process can be used to join different types of metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass. Oxy-acetylene welding is also used for brazing, soldering, and heating metal for bending and shaping.
3. Art
Oxy-acetylene welding is used in art to create sculptures, metal furniture, and other decorative pieces. The process allows for precise and intricate welding of metal pieces. The high temperature produced by the oxy-acetylene flame is ideal for welding and shaping metal sculptures.
Advantages and Limitations of Oxy-Acetylene Welding

Oxy-acetylene welding is a popular welding technique that has been used for over a century. This technique is widely used in the welding industry because of its numerous advantages. However, it also has its limitations. In this section, we will examine the pros and cons of using the oxy-acetylene welding technique.
Advantages of Oxy-Acetylene Welding
-
Versatile: Oxy-acetylene welding is a versatile process that can be used to weld a variety of metals, including steel, cast iron, copper, brass, and aluminum. This welding technique is also suitable for welding dissimilar metals.
-
Portability: Oxy-acetylene welding equipment is portable and can be used in remote locations where electricity is not available. This makes it an ideal welding technique for outdoor or on-site welding jobs.
-
Precise: Oxy-acetylene welding allows for precise control of the flame temperature, which makes it easier to control the weld pool and produce high-quality welds.
-
Low-cost: Oxy-acetylene welding equipment is relatively inexpensive compared to other welding techniques. This makes it an attractive option for small welding jobs or for welders who are just starting out.
Limitations of Oxy-Acetylene Welding
-
Limited Thickness: Oxy-acetylene welding is not suitable for welding thick materials. This is because the heat output of the flame is not sufficient to melt thicker materials, which can result in poor weld quality.
-
Limited Joint Strength: Oxy-acetylene welding produces weaker joints compared to other welding techniques. This is because the weld pool is not as deep as with other welding techniques, which can result in weaker welds.
-
Limited Weld Speed: Oxy-acetylene welding is a slower welding process compared to other welding techniques. This is because the heat output of the flame is not as high as with other welding techniques, which can result in longer welding times.
Safety Precautions in Oxy-Acetylene Welding
Oxy-acetylene welding is a process that requires proper safety precautions to prevent accidents. Here are some important safety measures and best practices to follow during oxy-acetylene welding:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Welding produces intense heat, bright light, and harmful gases. Therefore, it is essential to wear proper PPE to protect yourself from the hazards of welding. Here are some examples of PPE you should wear while oxy-acetylene welding:
- Welding helmet with a shaded lens
- Safety glasses with side shields
- Welding gloves and apron
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Respirator or other breathing protection
2. Ventilation
Oxy-acetylene welding produces harmful gases, including carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Therefore, it is essential to work in a well-ventilated area. Here are some ventilation tips to follow:
- Use a fume hood or exhaust fan to remove welding fumes from the work area.
- Keep the welding area well-ventilated by opening windows and doors.
- Do not weld in confined spaces without proper ventilation.
3. Fire Safety
Oxy-acetylene welding produces a flame that can cause fires. Therefore, it is essential to follow fire safety precautions to prevent fires. Here are some fire safety tips to follow:
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Do not weld near flammable materials.
- Keep a fire watch for at least 30 minutes after the welding is complete.
4. Equipment Safety
Oxy-acetylene welding equipment can be dangerous if not used properly. Therefore, it is essential to follow equipment safety precautions to prevent accidents. Here are some equipment safety tips to follow:
- Inspect the equipment before use to ensure it is in good condition.
- Use the correct tip size and pressure for the job.
- Always turn off the acetylene first when shutting down the equipment.
Step-by-Step Guide to Oxy-Acetylene Welding
Oxy-acetylene welding is a versatile welding process that requires a specific skill set and thorough practice. Here is a beginner-friendly guide to help you set up the equipment and perform basic welding tasks.
Step 1: Equipment Setup
Before you begin welding, you need to set up the equipment. Here are the steps to follow:
- Connect the acetylene and oxygen tanks to the welding torch using the appropriate hoses and fittings.
- Adjust the pressure on the regulators to the recommended levels for your specific welding task.
- Open the acetylene valve on the torch and ignite the flame using a striker or lighter.
- Adjust the size of the flame by adjusting the acetylene valve and the oxygen valve on the torch.
Step 2: Preparing the Metal
Before welding, you need to prepare the metal surfaces to be joined. Here are the steps to follow:
- Clean the metal surfaces using a wire brush or grinder to remove any rust, paint, or other contaminants.
- Clamp the metal pieces to be welded together in the desired position.
- Use a soapstone or other marking tool to mark the area to be welded.
Step 3: Welding
Now that you have set up the equipment and prepared the metal surfaces, you can begin welding. Here are the steps to follow:
- Position the torch at a 45-degree angle to the metal surface.
- Move the torch in a circular motion to create a puddle of molten metal.
- Add filler metal to the puddle as needed using a welding rod or wire.
- Move the torch along the joint, maintaining a consistent speed and distance from the metal surface.
- Continue welding until the joint is complete.
Step 4: Post-Welding
After welding, you need to perform some post-welding tasks. Here are the steps to follow:
- Allow the welded joint to cool down completely before handling it.
- Use a wire brush or grinder to clean up any excess weld material or slag.
- Inspect the joint for any defects or cracks.
- Apply a protective coating or paint to the welded joint if desired.
Troubleshooting Common Oxy-Acetylene Welding Problems
Oxy-acetylene welding is a popular welding technique that relies on the combustion of oxygen and acetylene gas to create heat for welding. However, like any welding method, oxy-acetylene welding can present some common problems that can affect the quality of the weld. Here are some tips and solutions for addressing these issues:
Problem: Porosity in Weld
Porosity in a weld can be caused by several factors, including contamination of the base metal, improper gas flow, or incorrect welding technique. To address this issue, try the following:
- Clean the base metal thoroughly before welding to remove any dirt, grease, or oil that might be present.
- Check the gas flow to ensure that it is correct and that there are no leaks in the hoses or fittings.
- Adjust your welding technique to ensure that you are using the correct flame size and angle.
Problem: Cracks in Weld
Cracks in a weld can be caused by several factors, including improper welding technique, improper preheating, or excessive stress on the weld. To address this issue, try the following:
- Adjust your welding technique to ensure that you are using the correct flame size and angle.
- Preheat the base metal to the correct temperature before welding to prevent thermal shock.
- Use proper welding techniques to minimize stress on the weld.
Problem: Warping of Base Metal
Warping of the base metal can be caused by excessive heat input or improper clamping. To address this issue, try the following:
- Use proper clamping techniques to prevent the base metal from warping during welding.
- Adjust your welding technique to minimize heat input to the base metal.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Difference Between Oxy Acetylene Welding and Arc Welding?
Oxy-acetylene welding and arc welding are two different welding processes. Oxy-acetylene welding uses a flame to heat and melt metal, while arc welding uses an electric arc to melt metal. Oxy-acetylene welding is typically used for welding thin metal sections, while arc welding is used for welding thicker metal sections.
How Do You Use Oxy-acetylene?
To use oxy-acetylene for welding, you need to have a welding torch, acetylene cylinder, oxygen cylinder, and welding rods. The torch is connected to the cylinders and the welding rods are inserted into the torch. The acetylene and oxygen are then turned on and adjusted to the correct proportions to produce the desired flame. The flame is then used to heat and melt the metal, while the welding rods are used to fill in the joint.
What is the Purpose of Oxygen in Oxy Acetylene Welding?
Oxygen is used in oxy-acetylene welding to provide the necessary heat to melt and join metal. When oxygen is combined with acetylene, it creates a flame that is hot enough to melt metal. The oxygen also helps to oxidize the metal, which helps to create a strong bond between the two pieces of metal.
What precautions should be taken when welding oxy-acetylene?
Always wear safety gear like gloves, a helmet, and protective clothes when oxy-acetylene welding. Check your tools for any leaks or damage before you start. Work in a place with good air flow and keep a fire extinguisher close by. Never use oil or grease on your welding tools, as this can cause fires. Light the acetylene before turning on the oxygen on your torch.
What is the 1/7 rule of oxy-acetylene?
The 1/7 rule says you shouldn't use more than one-seventh of an acetylene tank's contents in an hour. This rule keeps welding safe because acetylene can explode if used too fast. Following this rule helps prevent accidents and makes sure you're welding safely.





